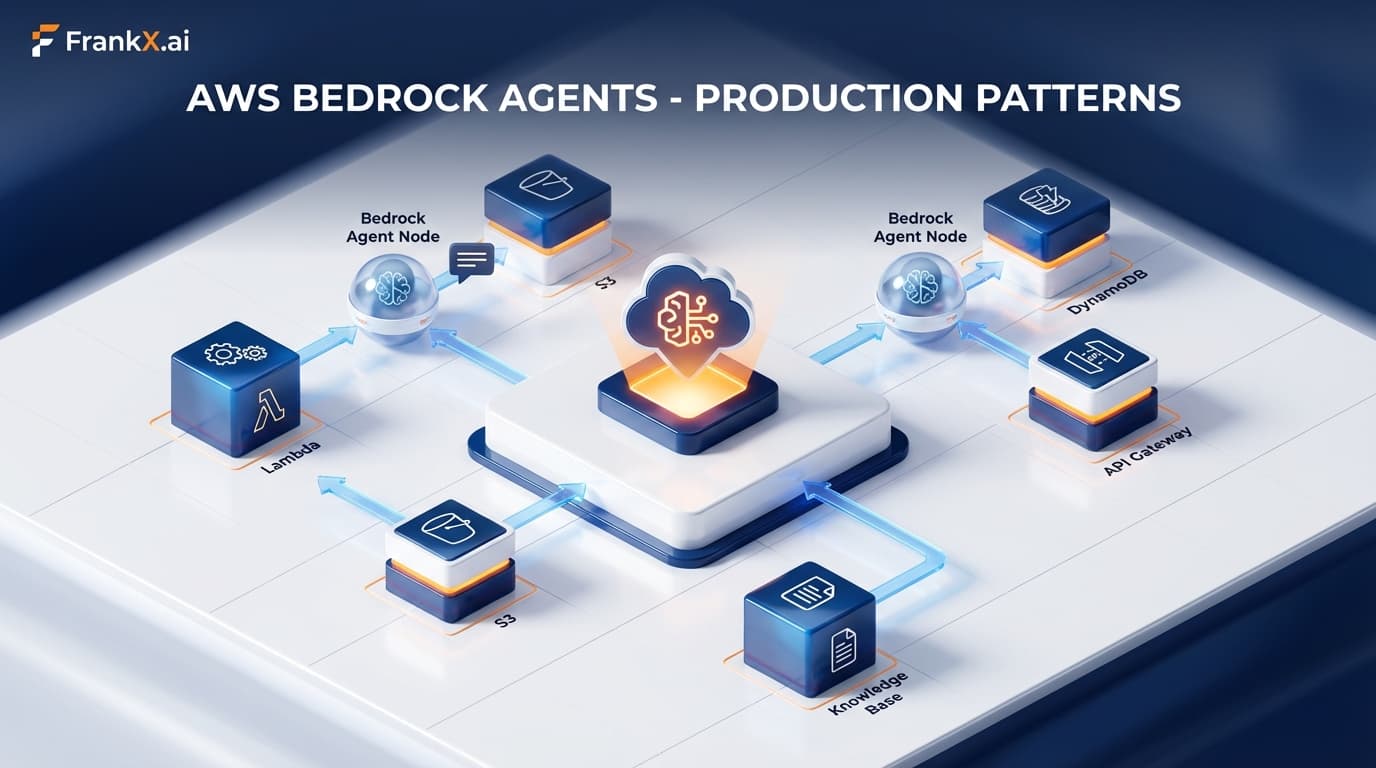
AWS Bedrock AgentCore Deep Dive: Production Patterns for Enterprise AI Agents
AI ArchitectureJanuary 21, 20269 min read
AWS Bedrock AgentCore Deep Dive: Production Patterns for Enterprise AI Agents
A comprehensive guide to building production-ready AI agents on AWS using Bedrock, AgentCore, and the Strands framework. Learn the architectural patterns, security controls, and operational best practices that power enterprise agent deployments.
TL;DR: AWS offers three tiers for building AI agents: Bedrock Agents (managed, no-code), AgentCore (framework-agnostic runtime), and Strands (open-source orchestration). The key differentiator is security-first design with IAM integration, Guardrails for content filtering, and managed memory that persists across sessions. Choose Bedrock Agents for quick deployment, AgentCore for production workloads, and Strands for complex multi-agent systems.
Part 2 of 8: Production Agent Patterns Series
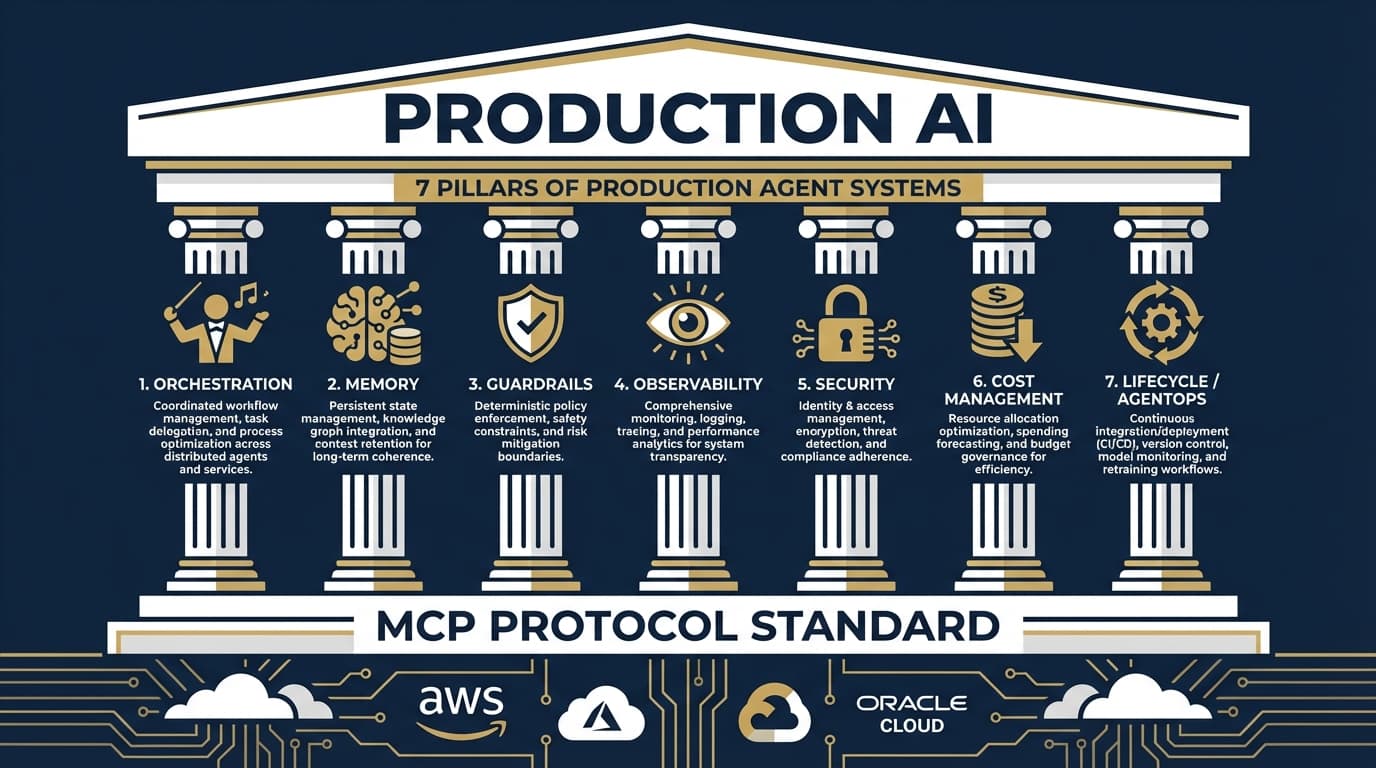
This is Part 2 of the Production Agent Patterns series. If you haven't read Part 1, start there for the 7 Pillars framework that guides this analysis.
Series Navigation:
- The 7 Pillars of Production Agent Systems
- AWS Bedrock AgentCore Deep Dive (this post)
- Google Vertex AI Agent Engine Deep Dive (coming soon)
- Azure AI Foundry Deep Dive
- OpenAI Agents SDK Deep Dive
- Claude Agent SDK Deep Dive
- MCP - The Unifying Standard
- Choosing Your Stack (Decision Guide)
AWS's Three-Tier Agent Architecture
AWS doesn't offer just one way to build agents—they offer three, each optimized for different use cases:

When to Use What
| Tier | Best For | Trade-off |
|---|---|---|
| Bedrock Agents | Rapid prototyping, simple use cases | Less flexibility |
| AgentCore | Production workloads, enterprise | More setup |
| Strands | Complex multi-agent, custom orchestration | Most complex |
Pillar 1: Orchestration with Strands
AWS's answer to multi-agent coordination is the open-source Strands framework. It provides three patterns:
Pattern 1: Swarms
Multiple agents work in parallel on the same task, with results aggregated.
from strands import Swarm, Agent
# Define specialized agents
researcher = Agent(
name="researcher",
model="anthropic.claude-sonnet-4",
instructions="You research and gather information."
)
analyst = Agent(
name="analyst",
model="anthropic.claude-sonnet-4",
instructions="You analyze data and find patterns."
)
# Create swarm
research_swarm = Swarm(
agents=[researcher, analyst],
aggregation="consensus" # or "vote", "merge"
)
# Execute
result = research_swarm.run("Analyze Q4 sales performance")
Pattern 2: Agent Graphs
Directed graphs with conditional routing between agents.
from strands import AgentGraph, Edge
graph = AgentGraph()
# Add nodes
graph.add_agent(intake_agent, node_id="intake")
graph.add_agent(research_agent, node_id="research")
graph.add_agent(write_agent, node_id="write")
graph.add_agent(review_agent, node_id="review")
# Add edges with conditions
graph.add_edge("intake", "research")
graph.add_edge("research", "write", condition=lambda s: len(s.sources) >= 3)
graph.add_edge("write", "review")
graph.add_edge("review", "write", condition=lambda s: s.needs_revision)
graph.add_edge("review", "END", condition=lambda s: s.approved)
# Execute
result = graph.run("Create a market analysis report")
Pattern 3: Workflows
Sequential pipelines with explicit state passing.
from strands import Workflow, Step
workflow = Workflow([
Step("gather", research_agent),
Step("analyze", analyst_agent),
Step("synthesize", writer_agent),
Step("validate", reviewer_agent),
])
result = workflow.run("Research quantum computing trends")
Pillar 2: Memory with AgentCore
AgentCore provides managed memory that persists across sessions—a key production requirement.
Memory Types
from bedrock_agentcore import Agent, Memory
agent = Agent(
model_id="anthropic.claude-sonnet-4",
memory=Memory(
# Short-term: conversation context
short_term_enabled=True,
short_term_window=10, # Last 10 messages
# Long-term: semantic extraction
long_term_enabled=True,
long_term_extraction="auto", # Auto-extract facts
# Session persistence
session_id="user-123-session-456",
persistence="dynamodb" # or "s3"
)
)
Semantic Memory Extraction
AgentCore automatically extracts and stores semantic information:
# After conversation, memory contains:
{
"user_preferences": {
"communication_style": "technical",
"timezone": "PST",
"role": "engineering_manager"
},
"learned_facts": [
"User's team uses Python for backend",
"Deployment target is EKS",
"Budget constraint: $10k/month"
],
"interaction_patterns": {
"peak_hours": "9am-11am",
"avg_session_length": "15min"
}
}
Pillar 3: Guardrails
AWS Bedrock Guardrails is the most comprehensive content filtering system across all providers.
Configuration
from bedrock import Guardrails
guardrails = Guardrails(
# Content filters
content_policy={
"hate": {"strength": "HIGH"},
"insults": {"strength": "MEDIUM"},
"sexual": {"strength": "HIGH"},
"violence": {"strength": "HIGH"},
},
# Topic blocking
denied_topics=[
"competitor_products",
"internal_financials",
"unreleased_features"
],
# PII handling
pii_config={
"action": "ANONYMIZE", # or "BLOCK"
"types": ["EMAIL", "PHONE", "SSN", "CREDIT_CARD"]
},
# Word filters
word_filters={
"profanity": "BLOCK",
"custom_words": ["secret_project", "codename_x"]
},
# Grounding check (hallucination prevention)
grounding={
"enabled": True,
"threshold": 0.7,
"source_required": True
}
)
# Attach to agent
agent = Agent(
model_id="anthropic.claude-sonnet-4",
guardrails=guardrails
)
The Action Router Pattern
AWS recommends keeping business logic OUTSIDE the model:

This pattern ensures:
- Predictable behavior: Your code controls execution
- Security: Validation happens in your code, not the LLM
- Auditability: Every action is logged and traceable
Pillar 4: Observability
AWS integrates with CloudWatch and X-Ray for comprehensive tracing.
CloudWatch Metrics
from bedrock_agentcore import Agent, CloudWatchMetrics
agent = Agent(
model_id="anthropic.claude-sonnet-4",
metrics=CloudWatchMetrics(
namespace="MyApp/Agents",
dimensions={"AgentName": "ResearchAssistant"},
metrics=[
"InvocationCount",
"Latency",
"TokensUsed",
"ErrorRate",
"GuardrailTriggered"
]
)
)
X-Ray Tracing
from aws_xray_sdk.core import xray_recorder
@xray_recorder.capture("agent_execution")
async def run_agent(query: str):
with xray_recorder.in_subsegment("tool_calls"):
result = await agent.run(query)
return result
What to Track
| Metric | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
InvocationLatency | User experience |
TokensPerInvocation | Cost management |
GuardrailBlockRate | Safety signal |
ToolCallSuccess | Reliability |
MemoryHitRate | Context effectiveness |
Pillar 5: Security
AWS's security model is the most mature, built on IAM integration.
Agent IAM Roles
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": ["bedrock:InvokeModel", "bedrock:InvokeAgent"],
"Resource": "arn:aws:bedrock:*:*:agent/*"
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": ["dynamodb:GetItem", "dynamodb:Query"],
"Resource": "arn:aws:dynamodb:*:*:table/AgentMemory",
"Condition": {
"ForAllValues:StringEquals": {
"dynamodb:LeadingKeys": ["${aws:PrincipalTag/AgentId}"]
}
}
}
]
}
Tool-Level Permissions
from bedrock_agentcore import Tool, Permission
# Define tool with explicit permissions
database_tool = Tool(
name="query_database",
description="Query the sales database",
permissions=Permission(
allowed_tables=["sales", "products"],
denied_tables=["users", "credentials"],
row_filter="department = ${user.department}",
max_rows=1000
)
)
Secrets Management
from bedrock_agentcore import Agent
import boto3
# Use Secrets Manager for API keys
secrets = boto3.client('secretsmanager')
agent = Agent(
model_id="anthropic.claude-sonnet-4",
tools=[
Tool(
name="external_api",
api_key=secrets.get_secret_value(
SecretId="prod/external-api-key"
)["SecretString"]
)
]
)
Pillar 6: Cost Management
AWS provides several cost optimization features:
Provisioned Throughput
For predictable workloads, reserve capacity:
# Reserve 100 model units for Claude Sonnet
# Saves ~30% vs on-demand for consistent usage
Prompt Caching
Bedrock automatically caches prompts with shared prefixes:
# System prompt (cached after first call)
SYSTEM_PROMPT = """You are a research assistant...
[2000 tokens of instructions]
"""
# User-specific context (not cached)
user_context = f"User: {user.name}, Role: {user.role}"
# This call benefits from caching
response = agent.invoke(
system=SYSTEM_PROMPT, # Cached
context=user_context, # Not cached
query=user_query # Not cached
)
Token Budgets
from bedrock_agentcore import Agent, TokenBudget
agent = Agent(
model_id="anthropic.claude-sonnet-4",
token_budget=TokenBudget(
max_input_tokens=10000,
max_output_tokens=4000,
max_total_per_session=50000,
on_exceed="graceful_stop" # or "error"
)
)
Cost Comparison
| Model | Input (per 1M) | Output (per 1M) | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Claude Sonnet 4 | $3.00 | $15.00 | Complex reasoning |
| Claude Haiku | $0.25 | $1.25 | Simple tasks |
| Llama 3.3 70B | $2.65 | $3.50 | Cost-sensitive |
Pillar 7: Lifecycle (AgentOps)
CI/CD with AWS CodePipeline
# buildspec.yml
version: 0.2
phases:
install:
commands:
- pip install -r requirements.txt
test:
commands:
- pytest tests/agent_tests.py -v
- python scripts/evaluate_agent.py --threshold 0.85
deploy:
commands:
- aws bedrock update-agent --agent-id $AGENT_ID --agent-config file://agent-config.json
Blue-Green Deployment
# Deploy new version alongside existing
new_agent = deploy_agent(config, version="v2")
# Gradual traffic shift
traffic_config = {
"v1": 90, # 90% to existing
"v2": 10 # 10% to new
}
# Monitor metrics, then shift
if new_agent.metrics.error_rate < 0.01:
traffic_config = {"v1": 0, "v2": 100}
Rollback
# Automatic rollback on error spike
if agent.metrics.error_rate > 0.05:
rollback_to_version("v1")
alert_team("Agent v2 rolled back due to high error rate")
Complete Example: Research Assistant on AWS
Here's a production-ready implementation:
"""
Research Assistant Agent - AWS Bedrock/AgentCore Implementation
Demonstrates all 7 pillars of production agent systems.
"""
import boto3
from bedrock_agentcore import Agent, Tool, Memory, Guardrails
from strands import Workflow, Step
# Pillar 5: Security - IAM-based configuration
session = boto3.Session(profile_name="production")
# Pillar 3: Guardrails
guardrails = Guardrails(
content_policy={"hate": {"strength": "HIGH"}},
pii_config={"action": "ANONYMIZE"},
grounding={"enabled": True, "threshold": 0.7}
)
# Pillar 2: Memory
memory = Memory(
short_term_enabled=True,
long_term_enabled=True,
persistence="dynamodb",
table_name="AgentMemory"
)
# Pillar 1: Orchestration - Tools
search_tool = Tool(
name="web_search",
description="Search the web for information",
handler=lambda q: search_api.search(q)
)
fetch_tool = Tool(
name="fetch_url",
description="Fetch content from a URL",
handler=lambda url: fetch_and_parse(url)
)
# Create agent
agent = Agent(
model_id="anthropic.claude-sonnet-4",
instructions="You are a research assistant...",
tools=[search_tool, fetch_tool],
memory=memory,
guardrails=guardrails,
# Pillar 6: Cost management
token_budget={"max_total": 50000},
# Pillar 4: Observability
metrics_namespace="ResearchApp/Agents"
)
# Pillar 7: Lifecycle - Versioning
agent.version = "1.2.0"
agent.deploy(environment="production")
When to Choose AWS
Choose AWS Bedrock/AgentCore if:
- You're already in the AWS ecosystem
- Security and compliance are top priorities
- You need enterprise-grade IAM integration
- You want managed memory persistence
- You're building multi-agent systems (Strands)
Consider alternatives if:
- You need provider portability (use OpenAI/Claude SDKs)
- You want simpler setup (use managed services)
- Cost is the primary concern (compare Llama hosting)
FAQ
How does AgentCore compare to Bedrock Agents?
Bedrock Agents is a managed, no-code solution for simple use cases. AgentCore is a framework-agnostic runtime for production workloads that need custom logic, multiple frameworks, or complex orchestration.
Can I use non-AWS models with AgentCore?
Yes. AgentCore is framework-agnostic. You can use models from Anthropic, Meta, Cohere, or even external providers via API integration.
What's the latency overhead of Guardrails?
Guardrails adds approximately 100-200ms to each request. For latency-sensitive applications, you can configure async guardrails that run in parallel with the main request.
How do I migrate from Bedrock Agents to AgentCore?
Export your agent configuration from Bedrock Agents, then import into AgentCore. AWS provides migration scripts that preserve memory and conversation history.
What's the cost of managed memory?
Memory uses DynamoDB under the hood. For most use cases, you'll stay within the free tier. High-volume applications typically see $5-20/month for memory storage.
Next in the Series
Part 3: Google Vertex AI Agent Engine Deep Dive
We'll explore Google's "agentic leap" vision, the Agent2Agent protocol, and how Model Armor provides security for production deployments.
Sources
- Amazon Bedrock Documentation
- AgentCore Developer Guide
- AWS Strands Framework
- Bedrock Guardrails
- Building AI Agents on AWS in 2025
- Multi-Agent Orchestration on AWS
Related Articles
- Production Agent Patterns: 7 Pillars — Framework-agnostic patterns
- Production LLM Agents on OCI — Oracle Cloud implementation
- Multi-Agent Orchestration Patterns — Coordination strategies
Related Research
Read on FrankX.AI — AI Architecture, Music & Creator Intelligence
Weekly Intelligence
Stay in the intelligence loop
Join 1,000+ creators and architects receiving weekly field notes on AI systems, production patterns, and builder strategy.
No spam. Unsubscribe anytime.